This article is synchronized and updated to xLog by Mix Space
For the best browsing experience, it is recommended to visit the original link
https://do1e.cn/posts/citelab/server-help
Tip
This document is updated irregularly, feel free to come back often to learn about the latest developments.
Click the directory on the right (scroll up on mobile, right bottom button) to jump to the content of interest
Connection and Login#
SSH connection or download the remote-ssh plugin for VSCode, search for specifics yourself.
::: banner {warning}
Starting from 2024.08.11, all servers will no longer allow password login. Please provide a public key when assigning a new account.
Send me the content of the public key (ssh-xxx xxxxx).
:::
Create a key pair:
# Try to use a longer key size to ensure security
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 8192
# It is more recommended to use a newer encryption algorithm
ssh-keygen -t ed25519
On Linux/Mac, it is saved by default in ~/.ssh/id_rsa or ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 (private key), ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub or ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub (public key).
On Windows, it is saved by default in the C:\Users\[username]\.ssh folder, with the same names.
The public key can be shared and should be saved in the server's ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file, with one public key per line corresponding to different PCs' private keys.
::: banner {warning}
Keep the private key safe and do not disclose it. It is strongly discouraged to use the same key on all your PCs!
Reference links:
- Using TPM for Secure SSH Key Authentication on Windows
- Password Management Service Bitwarden provided by Nanjing University
- SSH Key Hosting provided by Bitwarden
:::
You can configure ~/.ssh/config on your own computer as follows, so you can connect to the server directly using the ssh s1 command, which is more convenient.
Host s1
HostName s1.xxx.cn
Port 22
User xxx
IdentityFile xxx/id_rsa
For detailed tutorials, see: VSCode Configuration for SSH Connection to Remote Server + Passwordless Connection Tutorial
If you cannot connect using VSCode and it keeps prompting that it is downloading, you need to first connect via SSH and then log in to https://p.nju.edu.cn, refer to the following section on network issues.
Environment Configuration#
uv#
It is strongly recommended to use uv for project management environments. After configuring once, you can quickly complete the same environment configuration in different places, and the installation speed is much faster than conda and pip.
Related tutorial: Using uv to Manage Python Environments
After configuring the environment, run uv cache clean to clear the cache to alleviate space issues.
conda#
If you find conda: command not found, execute the following command and restart the terminal.
/opt/anaconda3/bin/conda init
Since the environment is saved in the ~/.conda directory, switching servers only requires copying the entire directory to complete the environment migration without needing to reconfigure. You can also edit ~/.condarc as follows and change envs_dirs and pkgs_dirs to /nasdata/[name]/.conda/[envs/pkgs], placing the environment configuration on NAS so that multiple services can use the same environment.
show_channel_urls: true
default_channels:
- https://mirror.nju.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main
- https://mirror.nju.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/r
- https://mirror.nju.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/msys2
custom_channels:
conda-forge: https://mirror.nju.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud
msys2: https://mirror.nju.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud
bioconda: https://mirror.nju.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud
menpo: https://mirror.nju.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud
pytorch: https://mirror.nju.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud
simpleitk: https://mirror.nju.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud
auto_activate_base: false
envs_dirs:
- ~/.conda/envs
pkgs_dirs:
- ~/.conda/pkgs
# Use Nanjing University's source for pip
pip config set global.index-url https://mirror.nju.edu.cn/pypi/web/simple
After configuring the environment, run conda clean --all and rm -rf ~/.cache/pip to clear a lot of unnecessary conda cache to alleviate space issues.
docker#
If the system software cannot meet the needs, you can use Docker. Specific tutorials can be searched and learned, but all Docker containers must be started with a normal user; otherwise, they will be cleared (lines 2-6 be retained, others can be customized as needed)
docker container run --name pytorch-dpj \
--gpus all \
--user $(id -u ${USER}):$(id -g ${USER}) \
-v /etc/passwd:/etc/passwd:ro \
-v /etc/group:/etc/group:ro \
-v /etc/shadow:/etc/shadow:ro \
-v /data1/peijie:/data/:rw \
-v /home/peijie:/home/peijie:rw \
-it fenghaox/pyt1.3cu10.1:v2 /bin/bash
Alleviating Home Space Issues#
conda clean --all: Delete conda cacherm -rf ~/.cache/pip: Delete pip cacheuv cache clean: Delete uv cachermoldvs: Delete old version of vscode-server
Check GPU Usage Status#
https://nvtop.njucite.cn/ (recommended)
Log in with your email. Please submit your email to the administrator to be added to the whitelist before you can access it.
Or use the nvtop command on each machine.
Use Specified GPU#
If parallelism is not enabled, PyTorch defaults to using GPU 0. If parallelism is enabled, it defaults to using all GPUs.
Before running the code, set the CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES environment variable to specify which GPU to use. For non-parallel use of GPU 1:
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1
Or for parallel use of GPUs 0-3:
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
Try learning multi-GPU parallel methods like DataParallel (which is relatively simple to implement but incurs extra memory overhead on the first GPU, leading to lower memory utilization) and DistributedDataParallel (which is more complex to implement and debug but more efficient; it is recommended to switch to this method after fixing the code).
nvtop can be used to check GPU usage. Coordinate with those who are using or occupying the GPUs.
Network Issues#
Proxy#
If a proxy is configured and there are network issues (like with GitHub), add proxychains before commands that require internet access, such as:
proxychains curl https://ipapi.do1e.cn/get-ip
Or use setproxy to set the proxy and then execute commands:
setproxy
curl https://ipinfo.io
unsetproxy
Both methods can be tried, but they do not guarantee effectiveness for all websites.
Logging into Campus Network#
If you need to log in to p.nju.edu.cn, refer to this project:
Github Repo not found
The embedded github repo could not be found…
uvx NJUlogin -i # Then scan the QR code to log in to the campus network
uvx NJUlogin -i -l pwdLogin # Or log in with username and password
uvx NJUlogin -p # Print user information
uvx NJUlogin -o # Log out
Mirrors#
Some mirrors are provided for access on campus. See NJU CITE Lab provided on-campus mirrors.
Running Code in the Background#
The server has tmux installed. To run code in the background (which can continue running after exiting the terminal), you only need to use the most basic features.
Type tmux new in the terminal to create a new terminal, execute long-running commands inside it, then press ctrl+B, followed by D to detach. At this point, the code continues to run in the background.
Alternatively, use tmux new -s <name> to specify a name for the new terminal, which defaults to a number starting from 0.
You can use tmux ls to view the names of terminals running in the background.
Use tmux attach -t <name> to return to that terminal to check the running status.
In the tmux terminal, press ctrl+B, then [ to enter scroll mode, where you can use the up and down keys to scroll, and press q to exit scroll mode.
Data!!!#
Data Storage Location#
::: warning
The home directory has limited space; do not place data files in the home directory. Please place them in /data1.
:::
Files that are not frequently used can be placed in /nasdata, see the NAS description section below for details.
Data Backup#
::: warning
Ensure the safety of your data on public servers.
:::
Rclone is installed on the server, and here is a backup method (to sync important files from the server to NJUBox):
rclone config
n → Custom configuration name (e.g., njubox) → 56 (seafile) → https://box.nju.edu.cn → Student ID → Password (enter y first, then enter the password twice) → 2fa (just press enter) → Database name (press enter to indicate all unencrypted databases) → Follow the prompts for the rest.
Common rclone Methods#
View Remote Files#
rclone ls [configuration name]:/[directory]

Sync#
The first run will copy all files (source address) to the remote (target address).
Subsequent runs will only copy changed and new files.
::: warning
Special Note: After each run, the files at the target address will be completely consistent with the source address. If files are deleted from the source address, running sync will also delete the corresponding files at the target address (using rclone copy will not delete files at the target address).
:::
rclone sync -v [source directory] [configuration name]:/[target directory]

Scheduled Sync#
Copy the above sync command and use crontab for scheduled tasks. Specifics can be searched online; there are many related tutorials.
NAS Description#
::: banner {warning}
NAS is not 100% reliable either; for important data, please follow the 321 principle (three copies, two media, one offline backup).
:::
Download the application from Synology's official website: Enterprise Cloud Storage | Synology Drive_Private Cloud_Access Data Anytime_Multi-Person Collaboration | Synology Inc.
Or access directly via the web: https://nas.njucite.cn:5001
IP/Domain: nas.njucite.cn
The application login to Drive will only show the home directory, which is only visible to you.
The web login will show the share directory, which is a shared directory mounted on each server at /nasdata, and can be used for data transfer between servers. Some (s4 and s5) servers have a 10G connection to NAS, while others are 1G.
::: warning
Everyone has access to /nasdata. To prevent accidental deletion by others, it is recommended to configure important data via rclone, refer to the section on Using rclone to Sync Local and NAS Files and remember to replace the URL.
:::
You can move files in the two directories via the web interface.

You can also mount using WebDAV, WebDAV address: https://nas.njucite.cn:5006
Use iperf3 to test connection speed:
iperf3 -c nas.njucite.cn

Using rclone to Sync Local and NAS Files#
rclone config
e/n/d/r/c/s/q> n # Create a new configuration
name> nas # Name the configuration nas
Storage> 52 # WebDAV, may vary with different rclone versions
url> https://nas.njucite.cn:5006 # It is recommended to use the 10G network on s4 and s5 servers with http://10.0.0.100:5005
vendor> 7 # Other site/service or software, may vary with different rclone versions
user> abcd # NAS username
y/g/n> y # Enter password
password: ... # Enter NAS password twice
# Just press enter for the rest
After creating the configuration on your local computer as described above, you can use the previously introduced rclone copy or rclone sync commands to sync files (e.g., upload local files to NAS or download NAS files to local).
::: warning
Special Note: After each run, the files at the target address will be completely consistent with the source address. If files are deleted from the source address, running sync will also delete the corresponding files at the target address (using rclone copy will not delete files at the target address).
:::
Advanced#
Auto-fill Previously Entered Commands#
You can use zsh as the default terminal and configure oh-my-zsh, powerlevel10k, zsh-autosuggestions, and zsh-syntax-highlighting.
zsh+oh-my-zsh+powerlevel10k terminal configuration_powerlevel10k configuration-CSDN Blog
Alternatively, you can directly use my configuration by extracting the following file into your home directory.
zshconfigs.tar.gz
GUI Related#
Some commands may prompt that there is no display. If you must use GUI and have no other options, you can refer to the following two methods. The first method is suitable for executing commands in your own terminal, while the second requires executing in MobaXterm. The former requires additional configuration, while the latter is ready to use.
Method One#
Install MobaXterm on your local computer and open the X server.

Hover the mouse over it to display [IP]:[x11port], select an IP and port that is not under router NAT (in Nanjing University, generally, non-NAT IP starts with 114 or 172, while IP under router NAT generally starts with 192.168 or 10) and enter the following in the server terminal:
export DISPLAY=[IP]:[x11port]
Then enter commands related to GUI, and click "Yes" in the pop-up window on your local computer.

Method Two#
Directly use MobaXterm to connect via SSH and execute GUI-related commands.
Copy with Progress Display#
Add the following to ~/.bashrc or ~/.zshrc:
function rcp(){
local src=$1
local dst=$2
if [ -f "$src" ] && [ -d "$dst" ]; then
dst="$dst/$(basename "$src")"
fi
mkdir -p "$(dirname "$dst")"
rsync -ah --info=progress2 "$src" "$dst"
}
After that, use rcp instead of cp. The logic is not completely the same; the second parameter dst should be the target directory and cannot be renamed like cp.
Send Email Notifications After Training Ends/Fails#
Add the following Python code at the end of your training script.
sender = "[email protected]" # Configure the sending email address
sender_name = "s1" # The name of the sender, defined as the server name here
passwd = "xxxxxxx" # Email password, if it's a QQ email, it's the authorization code
server = "smtphz.qiye.163.com" # The server of the sending email, for QQ email it's smtp.qq.com
port = 465 # The port number of the sending email, usually this one
receiver = "[email protected]" # The receiving email address
receiver_name = "Peijie Diao" # The name of the receiver
subject = "train on s3" # Email subject
message = "Training on s3 is finished" # Email content
import smtplib
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
from email.utils import formataddr
import socks
# The server cannot go online without logging in. I configured a proxy that allows local connections.
socks.set_default_proxy(socks.SOCKS5, "xxxx", 7891)
socks.wrapmodule(smtplib)
msg = MIMEText(message, 'plain', 'utf-8')
msg['From'] = formataddr((sender_name, sender))
msg['To'] = formataddr((receiver_name, receiver))
msg['Subject'] = subject
server = smtplib.SMTP_SSL(server, port)
server.login(sender, passwd)
server.sendmail(sender, [receiver], msg.as_string())
server.quit()
VPN Alternatives#
When the school's VPN server is unstable, consider using this, which is also relatively fast (provided that a successful P2P connection is established).
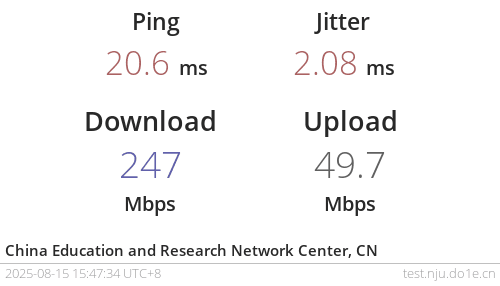
If capable, you can also consider setting up your own Zerotier or OpenVPN service.
Using Zerotier to Connect P2P with My Campus Server#
Refer to xubiaolin/docker-zerotier-planet-client configuration to configure Zerotier One (only focus on the Client Configuration section).
The planet file and network ID can be found by logging into https://nvtop.njucite.cn, or contact me. After configuration, contact me to provide the address for authentication.
The address is as follows: 15ffbcaa44
> zerotier-cli info
200 info 15ffbcaa44 1.14.2 ONLINE
After verification, restart the Zerotier service again, and you should obtain an IP address of 10.128.3.0/24, and be able to access https://test.nju.do1e.cn/. If this step is successful, proceed to the next step.
Allow Public Routing#
The following command requires administrator/sudo privileges. After completion, you should be able to connect to the server and NAS from off-campus and successfully access https://nvtop.main.njucite.cn.
zerotier-cli set {network ID} allowGlobal=1
The network ID can be found by logging into https://nvtop.njucite.cn, then restart the Zerotier service.
This method only ensures that the server and NAS can connect.
It is recommended to turn off when the laptop returns to school.#
Windows
Open services, find ZeroTier One, and change the startup type to manual, only manually start this service off-campus. Or change it to automatic, only manually stop this service on-campus.
Linux
sudo systemctl disable zerotier-one
# Then only manually start this service off-campus
sudo systemctl start zerotier-one
# Or allow it to start automatically
sudo systemctl enable zerotier-one
# Only manually stop this service on-campus
sudo systemctl stop zerotier-one